Spurious Correlations
Robust traing against spurious correlations
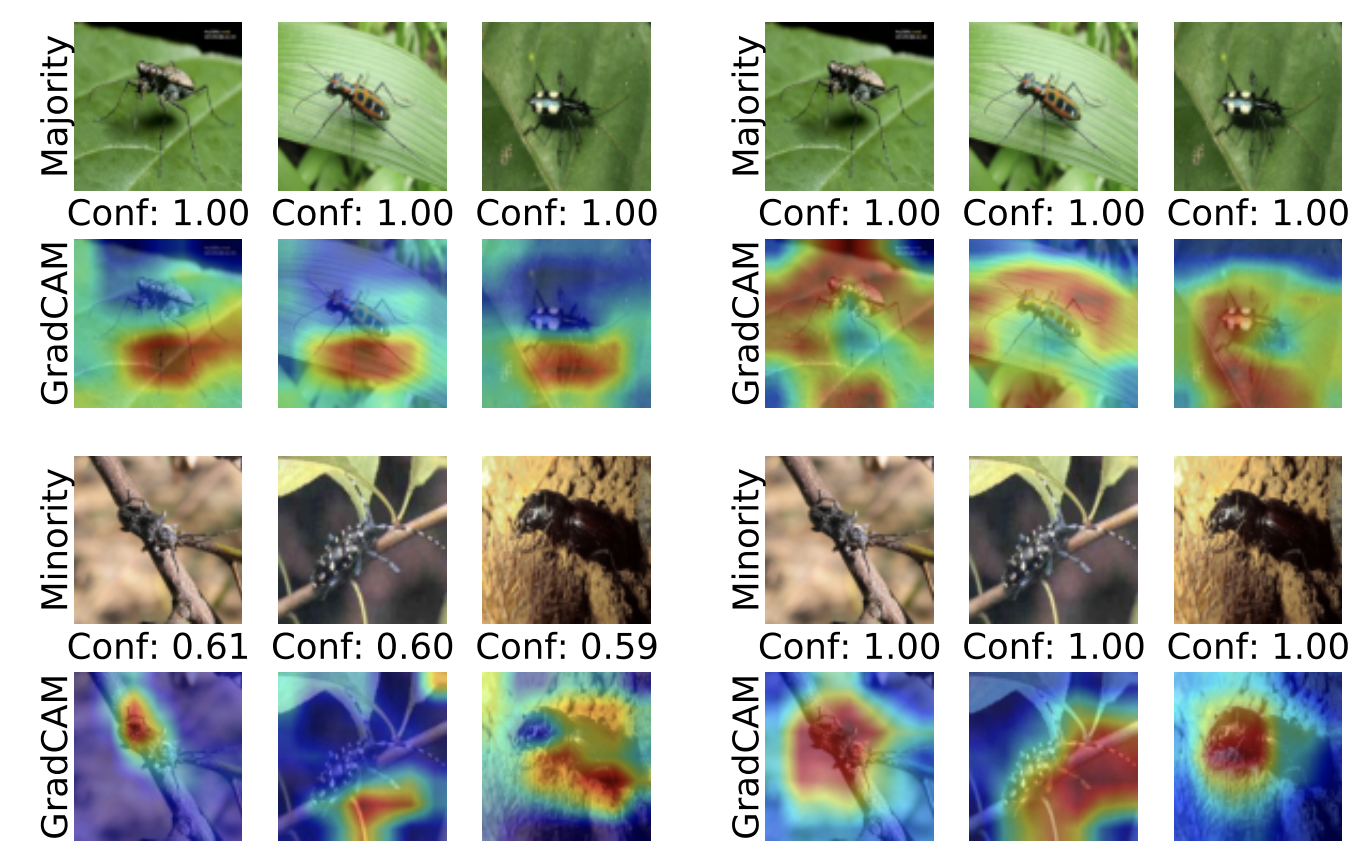
Neural networks are known to exploit spurious correlations in the training data: certain attributes that may correlate with certain categories during training, but are not predictive of the categories in general. For example, if the majority of lighter images co-occur with flame, the model may learn to associate the flame with the lighter category, rather than relying on the lighter to make the prediction. Similarly, a toxicity classifier may learn to spuriously associate toxicity with the mention of certain demographics in the text. Such biases degrade models’ worst-group test performance on minority groups that do not exhibit the spurious correlation.
We develop methods to mitigate the effect of spurious correlations during training neural networks. We consider robust training in supervised scenario, and mitigating spurious correlations from supervised or multimodal pretrained models during fine-tuning.
Checkout the following papers to know more: